In this
post I am going to write the step-by-step procedure to build an obstacle
avoiding Robot. I want to keep the cost of this Robot as low as possible so, I
am going to use cheap and easily available Sensors like IR LED and Photodiode
pair to detect the obstacles instead of expensive sensors like Sharp IR range
finder or Ultrasonic transducer. Even though I am using the inexpensive sensors
instead of expensive one the performance of the robot is good, you can find how
it works from the below You tube vedio –
Materials required:
1)
Arduino
2)
L293D Motor driver IC
3)
DC Motors (two)
4)
Wheels (two)
5)
Castor ball
6)
IR LED’s (at least 4)
7)
Photodiodes (at least 2)
9)
PCB board
11)
Connecting wires
12)
9 Volt Batteries (two)
13)
Double sided tape.
Step-by-step Procedure To Make an Obstacle Avoiding Robot:
preparing the Sensors:
I had said
before that, I am going to use IR LED’s and Photodiode as the Sensor to detect
the obstacles. If you don’t know How we to use IR LED’s and Photodiode pair to
detect the obstacles then, go through my previous post - How to use IR LED andPhotodiode pair with Arduino to detect obstacles.
For this
project I am going to use the same circuit which I had used in my previous post
but, I am going to add one extra IR LED to improve the sensor performance. So,
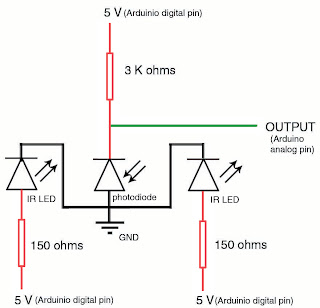
we need two IR LED’s and a Photodiode to prepare one sensor.
I had arranged the two IR LED’s and a Photodiode in the PCB board such
that the Photodiode is in the middle of two IR LED’s and I had soldered the component
(IR LED’s, Photodiode and resistors) which looks like this.
Each sensor has 5 wires two of them are
connected to two IR LED’s, one to the Photodiode, one common ground and one
wire is to take the readings from the sensor. The circuit diagram of the sensor
is shown below.
L239D Motor driver IC:
The L239D IC
is a motor driver which is used to control two DC motors at a wide range of supply
voltages (4.5 volts to 36 volts). Don’t connect the motors directly to
Microcontroller the sharp spikes from the motor may damage the Arduino. The
L239D IC has 16 legs. The connections of L239D with Arduino and DC Motors are
shown in the following picture.
Programming the Arduino:
The Arduino
source code for the Obstacle avoiding robot is presented below -
int enable=2;//Enable pins of L239D are connected to Arduino digital pin2int motA1=4;//pin-2 of L239D is connected to Arduino digital pin4int motA2=5;//pin-7 of L239D is connected to Arduino digital pin5int motB1=6;//pin-10 of L239D is connected to Arduino digital pin6int motB2=7;//pin-15 of L239D is connected to Arduino digital pin7int senA1=8;//sensorA first IR LED wire is connected to Arduino digital pin8int senA2=9;//sensorA second IR LED wire is connected to Arduino digital pin9int senA3=10;//sensorA Photodiode wire is connected to Arduino digital pin10int senB1=11;//sensorB first IR LED wire is connected to Arduino digital pin11int senB2=12;//sensorB second IR LED wire is connected to Arduino digital pin12int senB3=13;//sensorB Photodiode wire is connected to Arduino digital pin13int senAread=0;//wire connected between photodiode and 3 K resistor of sensorA is connectedto Arduino analog pinA0 int senBread=1;//wire connected between photodiode and 3 K resistor of sensorB is connectedto Arduino analog pinA1 void setup() { pinMode(enable,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(enable,HIGH); pinMode(motA1,OUTPUT); pinMode(motA2,OUTPUT); pinMode(motB1,OUTPUT); pinMode(motB2,OUTPUT); pinMode(senA1,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(senA1,HIGH); pinMode(senA2,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(senA2,HIGH); pinMode(senA3,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(senA3,HIGH); pinMode(senB1,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(senB1,HIGH); pinMode(senB2,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(senB2,HIGH); pinMode(senB3,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(senB3,HIGH); digitalWrite(motA1,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motA2,LOW);//In default mode both the motors will rotate forwarddigitalWrite(motB1,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motB2,LOW);//} void loop() { int val1=analogRead(senAread);// val1 variable stores the readings from sensorAint val2=analogRead(senBread);// val2 variable stores the readings from sensorBint diff=val1-val2;//calculating the difference of val1 and val2if(val1<800 || val2<800)//if any obstacle is detected by any one of the sensor{ if(diff>=0)//if obstacle is present at right side of the robot{ digitalWrite(motA2,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motA1,LOW);//make the bot move backwardsdigitalWrite(motB2,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motB1,LOW);//delay(1000);//wait for 1 seconddigitalWrite(motB2,LOW);//digitalWrite(motB1,HIGH);//turn leftdelay(700);//wait for 700 milli secondsdigitalWrite(motA1,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motA2,LOW);//move forward} else if(diff<0)//if obstacle is present at left side of the robot{ digitalWrite(motA2,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motA1,LOW);//make the bot move backwardsdigitalWrite(motB2,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motB1,LOW);//delay(1000);//wait for one seconddigitalWrite(motA2,LOW);//digitalWrite(motA1,HIGH);//turn rightdelay(700);//wait for 700 milli secondsdigitalWrite(motB1,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motB2,LOW);//move forward} } else//if no obstacle is present{ digitalWrite(motA1,HIGH);//digitalWrite(motA2,LOW);//digitalWrite(motB1,HIGH);// move forwarddigitalWrite(motB2,LOW);//} }
How program works:
The program starts with the initialization of variables. In the “void setup()” method the pin mode is set to output and the pins of sensors are made HIGH i.e., the sensors are at ON condition. Then the motors are made to move forward as a default state. In the “void loop()” method the values from the sensors are stored in variables ‘val1’ and ‘val2’ after that their difference is calculated and stored in the variable ‘diff’ which tells us whether the obstacle is present at the right side or left side (if diff is > 0 the obstacle is present at right side and if diff is < 0 the obstacle is present at the left side of the bot). An if-else ladder is used to make the robot turn according to the obstacle position. If an obstacle is present at the left side of the robot then the bot moves backwards a bit after that turn right side and the moves forwards. If the obstacle is present at right side of the bot then the bot moves backwards a bit after that turns left and then moves forward.Assembling:
Choose any available material for the chassis. I had used an aluminum
frame from an old DVD-ROM for the
chassis of the robot. Connect the sensors one at the right-front corner and the
other at the left-front corner of the chassis (you can add another sensor at
the middle of these two to increase the performance of the robot) by using a
double sided tape.
Attach the castor ball in the middle at the
front side of the robot with a double sided tape or any adhesive. Attach the
two DC motors in the back left and right positions by using double sided tape
or any adhesive. Then the bot will looks like in the below picture.
Connect the sensors according to the circuit
diagram shown above after that, connect the wires of L239D motor driver
according to the pin diagram of L239D IC which is shown above (be careful with
the directions of motor otherwise the bot will misbehave). After that Upload
the Arduino code into the Arduino Microcontroller. That’s it your bot is ready
for the first use.
Is this post useful? Please feel free to comment.
Is this post useful? Please feel free to comment.



yes this post is really useful
ReplyDeleteThanks for your feedback SRINIVAS
Deletecani use readymade IR sensor module
ReplyDeleteYes, you can use ready made IR sensor module. I just want to minimize the budget so that I made the sensors myself
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteIR sensor modules available in the market has 3 pins 1-Vin 2-Ground 3-analog output. Connect the Vin to digital output, connect ground pin to ground of Arduino and connect the analog output pin to analog pin of Arduino
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteConnect the Vin pins of both the sensors to digital output pins 8 & 9 of Arduino and remove the following lines from the code 8,9,10,11,26,27,28,29,30,31,32&33.
Deletethanks kranthi for ur patience thank u very much hope my project will success
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteInter change the wires of the motor which is not rotating in correct direction
DeleteIf you are still facing the problem then explain your problem more clearly or post a link to the vedio of your bot.
really this code is work
ReplyDeletebecause i want to drive my robot in bounded environment
I am happy with ur feedback
Deletesimple and nice
ReplyDeleteThanks Bharath
Deletevery nice..but wer is d complete ckt diagram..???
ReplyDeleteThe final circuit digram is nothing but connecting these two ckt's to Arduino according to the pin numbers mentioned in the two pictures. Try to connect these two circuit with the Arduino according to the pin numbers mentioned. If you still have any problem then drop a comment I will post the full circuit diagram.
Deleteplease post the complete ckt diagram...Thanks.
ReplyDeleteI am busy with my MID exams. I will post the complete ckt with in 2 or 3 days
Deletewhat would be the cost of arduino
ReplyDeleteCheck the latest prices of Original Arduino boards from - http://arduino.cc/en/Main/Products
DeleteCheck the prices of clone Arduino bords in India from - http://startrobotics.blogspot.in/2013/05/normal-0-false-false-false-en-us-x-none.html
is there any error in the code? because when I used it in my robot, the direction of the motors is not right.
ReplyDeleteI already fix this but when I change 800 to other value, the error with regards to direction returns.
DeleteThe value 800 doesn't have any direct or indirect relation to the direction of motors. The value 800 is only determines the detection range of obstacle. If you change the value from 800 to 700 or 600 or some other value less than 800 then the sensor detects the obstacle when the obstacle is much closer to the bot.
DeleteI would be happy, if you right something like remotely controlled robots even at a very basic level.
ReplyDeleteI will try
Deletei used sharp ir sensor and follow your instructions but the direction of the wheels are not correct/
ReplyDeleteinter-change the two motors i.e., left motor to right side and right motor to left
Deletei interchanged and the motors stopped
ReplyDeletethe motors are running but one side keeps getting forward then reverse repeatedly
Deletemotor turns to and fro means their might be some loose connections to the sensor. check for loose connections between sensor and arduino
Deletecan you please provide alternate code for utilization in a different microcontroller such as PIC ones...i am a beginner with microcontrollers so not very clear on code initialization and how much the syntax differs in different microcontrollers.
ReplyDeletesirt,i wanted to use ultrasonic distance measuring sensor,instead of this,can you please tell me that what changes i should made in your programme for this.link of this sensor is given below
ReplyDeletehttp://dx.com/p/hc-sr04-ultrasonic-sensor-distance-measuring-module-133696
If you want to build an obstacle avoiding bot using only one Ultrasonic sensor then its better to mount the sensor on Servo motor and scan for obstacles in 120 degrees. If you want me to post about that feel free to comment.
Deletehye..this post is really helpful..
ReplyDeletei'm thinking to apply your project with arduino line follower..
can you help me??
thank you very much..
Sure
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletei really appreciate it sir..
Deletegive me code for this project using 8051 as i m begineer in microcontroller
ReplyDeleteis programming necessary????
ReplyDeleteYup ( If you use Microcontroller)
Deletewe r trying to make obstacle avoider with rotating ir sensor...tell me something about it
ReplyDeleteIf you are trying to make a serious project (I mean not for hobby purpose) then its better to use Ultrasonic sensor or sharp IR sensor instead of normal IR led and photodiodes. because these sensors (Ultrasonic or Sharp IR sensors) performs better than normal IR led with photodiode.
DeleteFor the rotating purpose mount the sensor on a Servo motor.
If you need any further help (in terms of code or circuit diagram or anything related to your project) don't hesitate to ask me.
sir, can i ask permission from you if i can use this as my school project. and if you're willing. can you help me if i have some queries, thank you sir.
ReplyDeleteSure you can use this as your school project.
Deletedid you used 2 sensors(using IR and photodiodes)
ReplyDeleteYes
Deletei wanted to talk to you regarding this matter but i dont know how. do you have something that you know that we can talk easier?
ReplyDeleteyou can contact me via my facebook account https://www.facebook.com/kranthi.ind
Deletesir, done adding you on facebook. just wanted to know how did you connect the arduino with the dc motors and sensors, thank you in advance
Deletei sent you message on facebook already, hope you'll reply, really need your help :)
ReplyDeletesure
Deletethank all of you ,but help me, what i have to do if i will use two continuous servo motor rather than DC motor what i have to add or replace on the code and the circuit
ReplyDeleteIf you want to use Servo motors instead of DC motors then no need to use the L239D IC. You need to use the servo library to control the servo motors. just connect the red wire of your servo's to any Digital o/p pin and black wire to the Ground and the yellow/orange wire to PWM pin of your arduino and code the arduino accordingly
Deletecan you take a picture of the connection of the circuits, please. thanks
ReplyDeleteI have sent the pics to your fb profile
Deletedid you use breadboard? im wondering how did you connect the circuits. can you draw all the connections if its okay
ReplyDeleteIts not necessary to use bread board. You can solder the connections on pcb board
Deletehere's what i can say. our project wasnt able to work because maybe there's something wrong with the components because there is no available here. like the photodiode. but still, i want to thank the blogger, for helping me still to do our project. thumbs up for you sir. he's very approachable and very kind. ours didnt work but intend to help us, he even gave as alternative project.(coz we're chatting on fb. LOL) anyway. very long comment. i just wanna say thank you s omuch. sorry for late comment
ReplyDeleteis the polarity of photodiode is correct in the circuit diagram??????
ReplyDeleteyes, Photodiodes are made to use in Reverse bias condition
DeleteWill it be possible to use the L298 motor driver in place of the L293D motor driver?
ReplyDeleteyes you can use L298 but its connections may vary
Deleteyes sir this is very useful but please be in detail for the next time please just for the sake of beginners...!!!
ReplyDeletethanks for your feedback
DeleteHi!
ReplyDeletei am a school student, i liked your project very much,and i would like to use a hc-sr04 sensor mounted on a microservo. what changes should i do? Thanking You.
actually i am doing this project.on my own i have written codes but micro controller didn't get the input from sensor and executes the default case of my prog.i am using mikroc complier.do u have any suggesions regarding my prob.pls help me
ReplyDeleteon my own i have written codes . microcontroller doesn't accept input from sensor and drives the motor with default condition(specified in program) . i am using mikroc compiler.are u having any suggession regarding my problem ? pls help me if so
ReplyDelete